How Electric Vehicle Charging Works
Electric vehicle charging is the process of replenishing the energy stored in an electric vehicle’s battery. Understanding how electric vehicle charging works is fundamental for EV owners to effectively charge their vehicles and ensure they have sufficient range for their daily needs.
Types of Electric Vehicle Charging
There are three main types of electric vehicle charging: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging.
Level 1 Charging: Level 1 charging utilizes a standard household electrical outlet (120 volts) to charge an electric vehicle. It is the slowest charging method, typically adding about 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging. Level 1 charging is suitable for overnight charging at home or when there are no other charging options available.
Level 2 Charging: Level 2 charging operates at a higher voltage (240 volts) and requires a dedicated charging station. This charging method can add around 10-25 miles of range per hour, making it more suitable for daily charging needs. Level 2 charging stations can be installed at home, workplaces, and public locations, providing faster charging times compared to Level 1.
DC Fast Charging: DC Fast Charging, also known as Level 3 charging, is the fastest charging method available for electric vehicles. It uses high-voltage direct current (DC) to rapidly charge the vehicle’s battery. DC Fast Charging stations can add up to 200 miles of range in as little as 30 minutes, making them ideal for long-distance travel or quick top-ups. However, not all electric vehicles support DC Fast Charging, and dedicated charging stations are required.
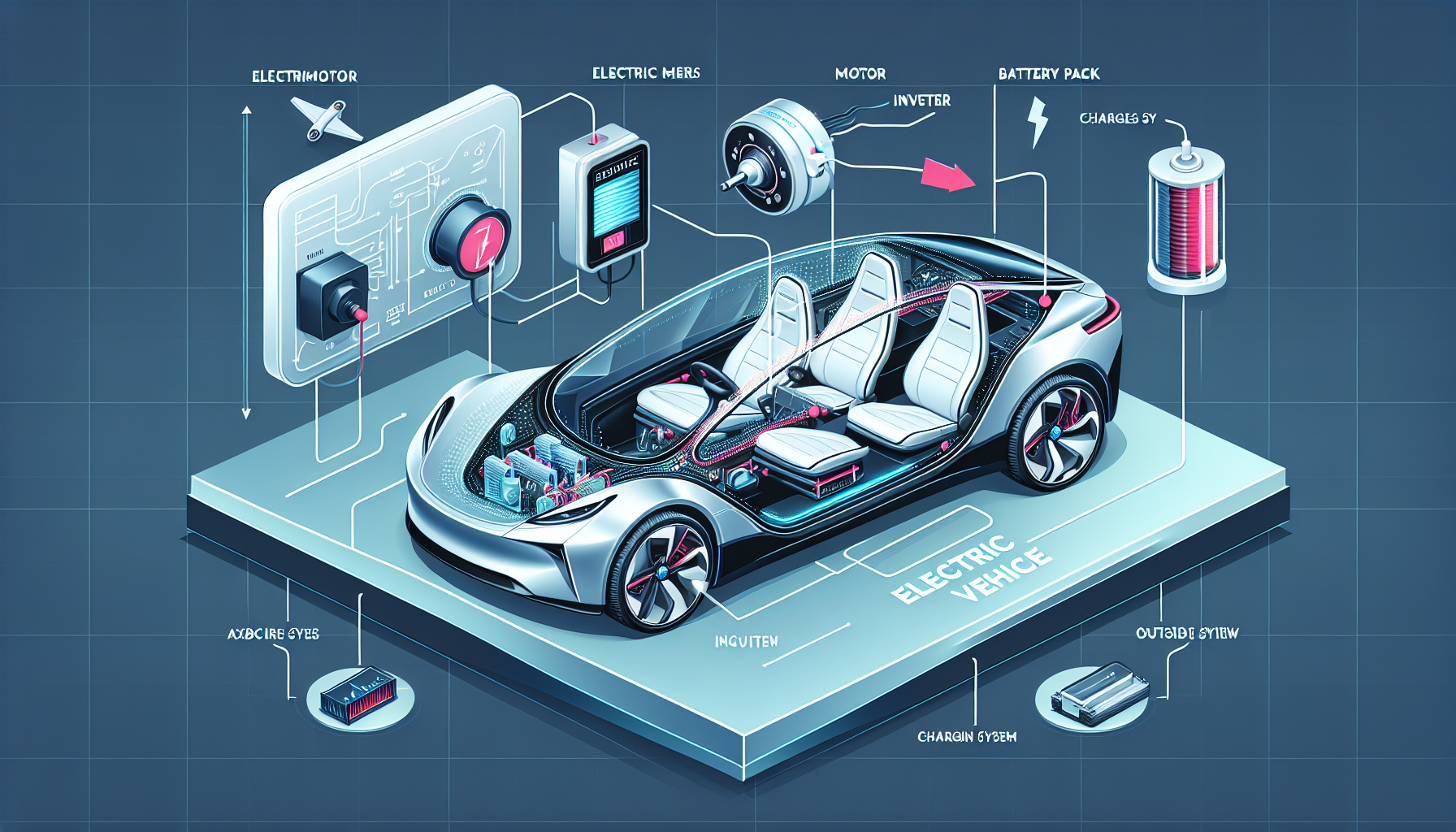
Components of an Electric Vehicle Charging System
Electric vehicle charging systems consist of several components that work together to facilitate the charging process:
Charging Station: A charging station, also known as an Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), is a device that connects to the electrical grid and provides power to the electric vehicle. Charging stations come in various forms, including wall-mounted units and standalone pedestals with multiple charging ports.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE): The EVSE manages the power flow between the charging station and the electric vehicle. It includes safety features such as ground fault protection and controls the charging process based on the vehicle’s specifications.
Charging Cable: The charging cable connects the charging station to the electric vehicle. It is available in different lengths and usually comes with a connector that fits the charging port on the vehicle.
Charging Connector: The charging connector is a component of the EVSE that physically connects to the electric vehicle’s charging port. It ensures a secure and reliable electrical connection during the charging process.
Charging Plug: The charging plug is the part of the charging cable that connects to the charging station or EVSE. It allows for the transfer of electricity from the charging station to the electric vehicle’s battery.
For more detailed information about electric vehicle charging, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Charging Method for Your Electric Vehicle
Choosing the right charging method for your electric vehicle is crucial to ensure convenient and efficient charging. Various factors should be considered when deciding which charging method suits your needs best.
Factors to Consider
When selecting a charging method, consider the following factors:
1. Vehicle Battery Size: The size of your electric vehicle’s battery will determine how much energy it can store. Larger batteries may require faster charging methods to meet your range requirements.
2 here. Daily Commute and Driving Routine: Assess how far you typically drive in a day. If you have a shorter daily commute or regular access to charging, slower charging methods like Level 1 or Level 2 may be sufficient. However, if you frequently drive long distances, DC Fast Charging may be necessary to quickly replenish your battery.
3. Available Charging Infrastructure: Evaluate the availability of charging stations in your area. If there are numerous Level 2 or DC Fast Charging stations nearby, you’ll have more flexibility in your charging options.
4. Time Considerations: Consider how much time you can dedicate to charging. Level 1 charging is the slowest method, while DC Fast Charging is the fastest but requires dedicated charging stations.
Comparison of Charging Methods
Here is a comparison of the different electric vehicle charging methods:
Charging Method
Level 1 Charging
– Voltage: 120 volts
– Typical Range Added Per Hour: 2-5 miles
– Best Suited for: Overnight charging at home or when no other options are available
Level 2 Charging
– Voltage: 240 volts
– Typical Range Added Per Hour: 10-25 miles
– Best Suited for: Daily charging needs, including home, workplace, and public locations
DC Fast Charging
– Voltage: High-voltage direct current
– Typical Range Added Per 30 Minutes: Up to 200 miles
– Best Suited for: Long-distance travel or quick top-ups
It’s important to note that the availability and suitability of each charging method may vary depending on your electric vehicle’s make and model. Consult your vehicle’s manual or contact the manufacturer for specific charging recommendations.
Here’s a summary of the different charging methods:
Charging Method Comparison Table:
Charging Method | Voltage | Typical Range Added Per Hour
Level 1 Charging | 120 volts | 2-5 miles
Level 2 Charging | 240 volts | 10-25 miles
DC Fast Charging | High-voltage DC | Up to 200 miles (30 minutes)
For a complete comprehensive guide on electric vehicle charging, feel free to refer to the following table:
Electric Vehicle Charging Methods – Comparison Table
| Charging Method | Voltage | Typical Range Added Per Hour |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Charging | 120 volts | 2-5 miles |
| Level 2 Charging | 240 volts | 10-25 miles |
| DC Fast Charging | High-voltage DC | Up to 200 miles (30 minutes) |
By considering these factors and understanding the capabilities and limitations of each charging method, you can make an informed decision on the most suitable charging method for your electric vehicle.
Best Practices for Electric Vehicle Charging
Adhering to best practices for electric vehicle charging can help optimize the charging experience, ensure safety, and maximize the efficiency of your electric vehicle’s battery.
Charging Etiquette
When using public charging stations or sharing charging infrastructure with others, it is essential to follow proper charging etiquette:
1. Sharing Charging Stations: Be considerate of other electric vehicle owners and avoid hogging charging stations once your vehicle is adequately charged. Move your vehicle promptly to free up the charging spot for others.
2. Proper Use of Charging Cables: Handle charging cables with care and make sure they are properly connected to both the charging station and your electric vehicle. Avoid tripping hazards by neatly organizing the cable and keeping it away from paths and walkways.
3. Charging Station Etiquette: Respect any guidelines or instructions provided by the charging station host. Be mindful of any time limits, fees, or rules associated with the charging facility.
Tips for Charging Efficiency
To optimize the efficiency of your electric vehicle charging, consider the following tips:
1. Charging at Optimal Times: Taking advantage of off-peak electricity rates or charging during periods of lower electricity demand can potentially save you money. Consult your local utility provider to determine the best charging times.
2. Maximizing Battery Health: Avoid charging your electric vehicle battery to its maximum capacity on a regular basis as it can put extra strain on the battery’s longevity. Instead, aim to charge your vehicle to around 80% or follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
3 2023-대박-예감-요즘-뜨는-레인-부츠-10-미리-보기. Utilizing Vehicle Features for Efficient Charging: Some electric vehicles come equipped with features that allow you to schedule or set charging limits. Take advantage of these features to ensure that your vehicle is charged when needed while avoiding unnecessary power consumption.
Following these best practices will not only enhance your charging experience but also contribute to the long-term health and performance of your electric vehicle battery.
If you have any additional questions or concerns about electric vehicle charging, here are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Common Questions about Electric Vehicle Charging
How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle?
The charging time for an electric vehicle depends on several factors such as the battery size, charging method, and the charging station’s power output. Level 1 charging typically takes the longest, while DC Fast Charging offers the fastest charging times, usually providing a significant range boost in as little as 30 minutes.
Can I charge an electric vehicle in the rain?
Yes, electric vehicles are designed to withstand various weather conditions, including charging in the rain. The charging ports and connectors are built to be weather-resistant and provide safe charging even in wet conditions. However, it is essential to ensure that the charging station is properly installed and is in good working condition to maintain safety.
What happens if I leave my electric vehicle plugged in for too long?
Modern electric vehicles are equipped with sophisticated battery management systems that prevent overcharging. Once the battery reaches its full capacity, the charging process will stop automatically. Leaving your vehicle plugged in after reaching a full charge will not cause any damage to the battery.
How much does it cost to charge an electric vehicle?
The cost of charging an electric vehicle depends on the electricity rates in your area, the charging method used, and the capacity of your vehicle’s battery. On average, electric vehicle owners can expect to pay less per mile driven compared to gasoline-powered vehicles.
Can I use a charging station from a different manufacturer?
Yes, most charging stations support vehicles from various manufacturers as long as the connector and charging standards match. Most electric vehicles in the market use either the CCS (Combined Charging System) or CHAdeMO charging standards for DC Fast Charging, while Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations typically use standard connectors that fit all electric vehicles.
By familiarizing yourself with these common questions and their answers, you will be better prepared to navigate the world of electric vehicle charging and make informed decisions as an electric vehicle owner.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric vehicle charging is a vital aspect of owning an electric vehicle. By understanding the different types of charging methods, the components of a charging system, and factors to consider when choosing the right charging method, you can effectively charge your electric vehicle and ensure you have sufficient range for your needs.
By following best practices for electric vehicle charging, such as practicing charging etiquette and maximizing charging efficiency, you can optimize your charging experience and contribute to the longevity of your electric vehicle’s battery.
Remember to consider factors such as your vehicle’s battery size, daily commute, available charging infrastructure, and time considerations when choosing the most suitable charging method. Level 1 charging is suitable for overnight charging, Level 2 charging offers faster daily charging, and DC Fast Charging is ideal for long-distance travel or quick top-ups.
For more detailed information about electric vehicle charging, make sure to consult the infographic below:
Electric Vehicle Charging Methods – Comparison Table
| Charging Method | Voltage | Typical Range Added Per Hour |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Charging | 120 volts | 2-5 miles |
| Level 2 Charging | 240 volts | 10-25 miles |
| DC Fast Charging | High-voltage DC | Up to 200 miles (30 minutes) |
With these insights and information, you are well-equipped to navigate the world of electric vehicle charging and make informed decisions as an electric vehicle owner. Embracing electric vehicle charging not only benefits you in terms of cost savings and convenience but also contributes to a more sustainable future.
So, embrace electric vehicle charging, reduce your carbon footprint, and join the growing community of electric vehicle enthusiasts who are shaping the future of transportation.
Introduction
The market for electric vehicles (EVs) has been rapidly growing in recent years, with an increasing number of people opting for these environmentally-friendly transportation options. However, as with any new technology, there are often questions and concerns surrounding certain aspects of EV ownership. One of the most common areas of confusion is around electric vehicle charging. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to electric vehicle charging, covering everything you need to know to confidently and efficiently charge your EV.
Why is Electric Vehicle Charging Important?
Before diving into the details of EV charging, it is important to understand why it is such a crucial aspect of EV ownership. Electric vehicle charging plays a vital role in keeping your EV on the road and ensuring that it has sufficient power for your daily needs. A well-planned and efficient charging routine can help you avoid range anxiety, reduce your reliance on fossil fuels, and save money on fuel costs.
With the right knowledge and understanding, utilizing the various types of EV charging and making informed choices related to charging infrastructure and practices can significantly enhance your EV ownership experience. So, let’s delve into the details of electric vehicle charging and explore the different aspects you need to be aware of.
How Electric Vehicle Charging Works
Understanding how electric vehicle charging works is essential for any EV owner. Essentially, the charging process involves transferring electricity from an external power source to your EV’s battery for storage and later use. Here is a breakdown of the key components involved in the process:
Types of Electric Vehicle Charging
There are several types of electric vehicle charging methods available, each with its own characteristics and charging speeds. The most common types include Level 1 Charging, Level 2 Charging, and DC Fast Charging. Let’s take a closer look at each:
Level 1 Charging: This is the most basic form of EV charging and utilizes a standard household outlet (120 volts) to charge your vehicle. While it is the slowest charging option, it is convenient for overnight charging at home or when no other charging options are available.
Level 2 Charging: Level 2 charging operates at a higher voltage (typically 240 volts) and requires a dedicated charging station. Level 2 charging provides faster charging speeds compared to Level 1, making it ideal for regular daily charging needs. It can add anywhere from 10 to 25 miles of range per hour of charging.
DC Fast Charging: DC Fast Charging, also known as Level 3 charging, is the fastest charging option available for EVs. It utilizes high-voltage DC power to deliver a rapid charge to your vehicle’s battery. DC Fast Charging stations can add up to 200 miles of range in as little as 30 minutes, making them ideal for long trips or quick top-ups.
Components of an Electric Vehicle Charging System
An efficient electric vehicle charging system comprises several important components that work together to ensure safe and reliable charging. These components include:
Charging Station: Also known as an Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), the charging station is the physical unit that delivers electricity to your vehicle. It connects to a power source and regulates the charge flow based on communication with your vehicle’s onboard systems.
Charging Cable: The charging cable connects your EV to the charging station. It allows for the transfer of electricity, enabling charging to take place. Charging cables come in different lengths and connector types depending on the charging station and EV specifications.
Charging Connector: The charging connector is the component that physically connects your EV to the charging cable. It ensures a secure electrical connection and is designed to be compatible with your specific vehicle model and charging standards.
Charging Plug: The charging plug is the component at the end of the charging cable that connects to the charging station or EV. It allows for the transfer of electricity between the two, ensuring a reliable and efficient charging process.
By understanding the different types of EV charging and the components involved, you have laid the groundwork for efficiently charging your electric vehicle. In the next sections, we will explore how to choose the right charging method for your specific needs and provide best practices for a seamless charging experience.